By: Lindsey Decker, SPT
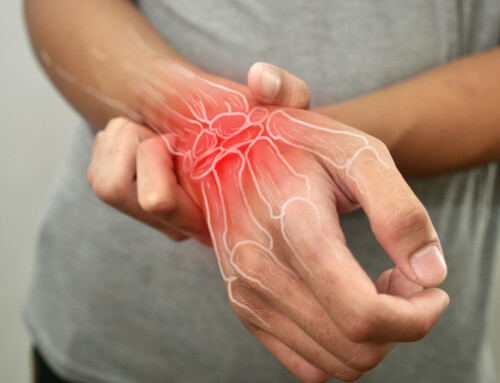
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) most likely does not happen from a single event but rather a series of dysfunction which causes symptoms when it reaches its critical state. The carpal tunnel is a small space on our wrists front side containing nine tendons and the median nerve. CTS is compression of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel of the wrist. The compression of the median nerve can be due to narrowing of the area within the carpal tunnel, crowding of tendons, inflammation, or injury. It is often seen in females more than males, which is thought to be due to women having a smaller carpal canal.
○ Acute CTS is less common and is directly associated with fractures, dislocations, and vascular disorders of the wrist.
○ Chronic CTS is more common and can be described as pain, paresthesia, numbness, tingling, burning sensation, and weakness to the median nerve distribution, which includes the palm, thumb, pointer finger, middle finger, and half of the ring finger.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Many causative factors contribute to CTS, but it is most commonly associated with performing repetitive activities and to what degree the hand is positioned, and the amount of load on the hand. Prevalence increases in tasks that require gripping, holding tools or steering wheels that vibrate, lifting more than 26 pounds, working in extremely cold environments, or a lot of finger use, such as typing.
CTS can also occur in individuals who experience diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, toxic exposure, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid tenosynovitis, edema, pregnancy, hypothyroidism, and congestive heart failure. Physically inactive individuals, obese individuals with a BMI greater than 29, and smoking cigarettes.
Presentation and Progression
It is more common to notice symptoms at night during the early stages. Individuals often report their sleep is disrupted due to the numbness and tingling sensation. Some individuals state that shaking their hand out helps relieve symptoms. The pain may radiate into the palm and up the forearm and arm. As CTS progresses, individuals report that symptoms are noticeable during the day and are often worse when holding objects such as a toothbrush or a pen. Individuals have also stated that they may drop things unexpectedly due to the weakness in their grip strength.
Carpal Tunnel Treatment
Early management
○ Ergonomic modifications: wrist positioning, keyboard positioning, wrist rest, and overall workstation
○ Lifestyle changes: no alcohol, no smoking, management of diabetes, active lifestyle, keep your hands warm, take breaks during repetitive activities.
● Long-term usage of anti-inflammatory medications should be avoided due to gastric complications without significant changes in symptoms.
● Steroid injections into the carpal canal – may relieve symptoms for up to a year.
● When symptoms have persisted for over a year, and motor and sensory loss is indicated, surgical release of the transverse carpal ligament.
○ 76% experience normal two-point discrimination post-surgery
○ 70% return to their normal grip strength post surgery
○ Nerve and tendon gliding is advocated post-surgery to help minimize scarring and adhesions to help decrease the formation of fibrotic tissue.
● Physical Therapy
○ Ergonomic modifications, postural changes, education on taking stretch breaks during repetitive motion activities, exercises to help improve strength and flexibility of the wrist, hand, and fingers, and use of modalities provided by the physical therapist.
References
1. Dutton M. Dutton’s Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, and Intervention.; 435, 795
2. Goodman C, Fuller K. Pathology Implications for the Physicla Therapist.; 1668-1672
3. Heick J, Lazaro RT. Goodman and Snyder’s Differential Diagnosis for Physical Therapists Screening for Referral.; 417- 418
4. Trillos-Chacón MC, Castillo-M JA, Tolosa-Guzman I, Sánchez Medina AF, Ballesteros SM. Strategies for the prevention of carpal tunnel syndrome in the workplace: A systematic review. Applied ergonomics. 2021;93:103353-103353
Capital Area Physical Therapy & Wellness offers treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome. Our experienced providers serve the Upstate NY Malta / Saratoga / Glens Falls & Queensbury region with physical therapy services for carpal tunnel syndrome.
Call (518) 289-5242 to schedule an evaluation at any of our locations, or to learn more about the services provided by our physical therapists.