By: Samantha Resende, SPT
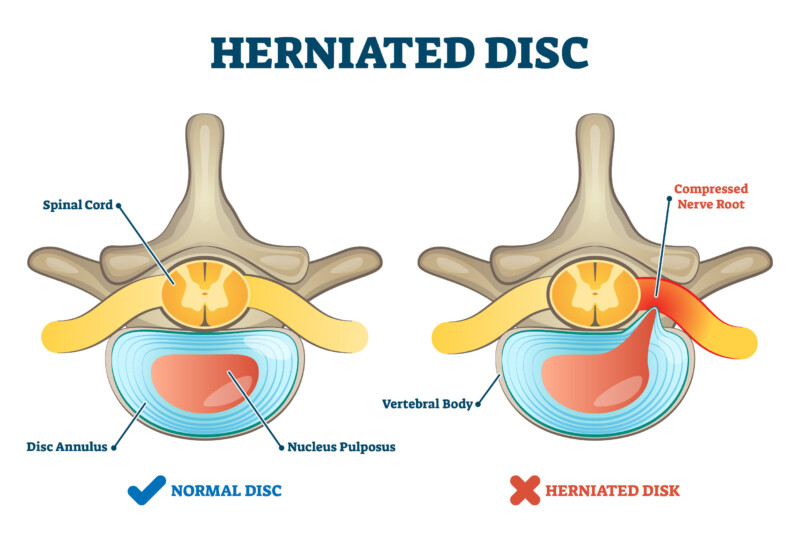
A herniated disc is when the rubbery cushion of the spine is being pushed out externally. This can be due to a weakened or cracked part of the disc. A herniated disc is a common condition that can occur throughout the spine. The most common location of a herniated disc is the lower back.
Presentation of Herniated Disc:
Anatomy:
The spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae bones being stacked onto each other to create a protective canal. The spine is consisted of nerves that act out as messenger cables to rely on information from the brain to the muscles, and vice-versa. In between each vertebra there are intervertebral discs that acts as shock absorbers during body movements. A herniated disc starts when the center of the disc (nucleus pulposus) is being pushed out of the outer ring (annulus fibrosus) creating pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. The compression on the spinal nerves can be irritated and present nerve inflammation which can lead to pain and other symptoms.
Cause:
A herniated disc can be a result of age, wear and tear of the spine, or disc degeneration. With age, the water content in the disc starts to decrease and lead to less spine flexibility. This process contributes to the decreased space or narrowing in between each vertebra. This is a normal aging process that contributes to an increase chance of obtaining a herniated disc.
Other risk factors are improper lifting, traumatic event (falls), higher body mass index (BMI), smoking, sedentary lifestyle, and repetitive activities/motion that can strain the spine.
Signs and Symptoms of a herniated disc:
When the nerves are irritated, it can cause pain. The most common symptom associated with a herniated disc is lower back pain. The symptoms are associated with the location of the herniation. Pain can be described as a dull ache or sharp radiating pain. A sharp radiating/shooting pain can start around the buttocks area and go down towards the back of a leg. Other symptoms can include numbness or tingling (pins and needles) sensation down a leg towards the foot, leg and/or foot weakness, muscle spasms, rarely loss of bladder or bowel control. A person may have trouble bending or rotating their neck or back, increased pain with couching, sneezing, prolong sitting, difficulty getting up from a chair, stiffness, and pain worse in the morning.
Herniated Disc Treatment Options:
Screening:
A physician or primary care doctor will perform a physical examination and intake medical history based on the presenting symptoms. The examination may include testing muscle strength/weakness, loss of sensation, and reflexes. Imaging can be recommended, such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to provide clear picture of the spine and the intervertebral disc. An MRI can assist in diagnosing herniated disc and the affected spinal nerves.
Treatment recommendations:
- Recovery is dependent on the patient, majority of patients will slowly improve over time, while others may experience a fluctuation of pain.
- Non-surgical treatment plans can include rest, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), epidural steroid injections, and physical therapy. A physical therapist will provide patients with specific exercises to strengthen abdominal and lower back muscles to improve pain, restore function, and return to regular activities.
- Surgical treatment can be recommended for patients who did not obtain symptoms relief from non-surgical treatment.
References:
1. Amin RM, Andrade NS, Neuman BJ. Lumbar Disc Herniation. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017;10(4):507-516. doi:10.1007/s12178-017-9441-4
2. Zeller JL, Burke AE, Glass RM. Herniated Lumbar Disks. JAMA. 2006;296(20):2512. doi:10.1001/jama.296.20.2512
3. When you have a herniated disc. (Information from Your Family Doctor). American family physician. 2003;67(10).
4. Hancock M, Koes B, Ostelo R, Peul W. Diagnostic Accuracy of the Clinical Examination in Identifying the Level of Herniation in Patients with Sciatica. Spine (Philadelphia, Pa 1976). 2011;36(11):E712-E719. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181ee7f78
Capital Area Physical Therapy & Wellness offers treatment options for herniated discs. Our experienced providers serve the Upstate NY Malta / Saratoga / Glens Falls & Queensbury region with physical therapy services for herniated disc symptoms.
Call (518) 289-5242 to schedule an evaluation at any of our locations, or to learn more about the services provided by our physical therapists.